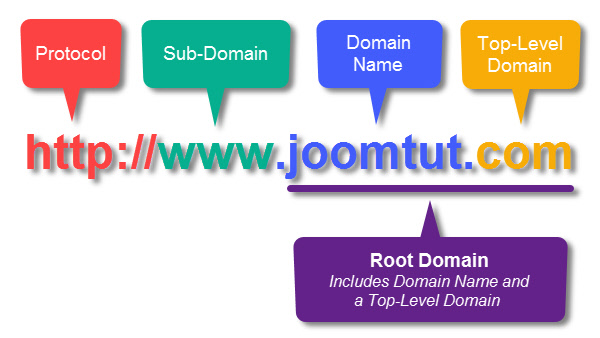
What is a domain name
Domain name is an unique, human-readable internet address of a website. It is made up of three parts: a top-level domain, sometimes called an extension or domain suffix, a domain name or IP address and an optional subdomain.
Protocol
The http:// is part of a page's URL but not its domain name and is known as the protocol
In domain name, protocol is a way of transmitting data on the internet. In particular, the HTTP - Hypertext Transfer Protocol is an application protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTPS - Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure is an extension of the hypertext transfer protocol - HTTP. It is used for secure communication over a computer network and is widely used on the Internet. FTP - File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of computer files between a client and server on a computer network.
Subdomain
Subdomain are the third level of a domain's hierarchy and are parts of a larger top-level domain. It is added in front of the root domain and separated from the domain name with a period.
Domain name
Domain names are the second level of a domain's hierarchy - after the top-level domain. Domain names on a specific TLD - called a root domain, discussed below are purchased from registrars and represent the specific, unique location of a website.
Top-level domain
A top-level domain - TLD is one of the domains at the highest level in the hierarchical Domain Name System - DNS of the Internet. The top-level domain names are installed in the root zone of the name space. Top-level domain is the formal term for the suffix that appears at the end of a domain name.
Generally, you can divide TLDs into two types:
- Generic top-level domains (gTLD) - Roughly all domains that are not associated with a country. The most known are com, org and net. All gTLDs fall under ICANN's policies.
- Country-code top-level domains (ccTLD) - All domains that are identified with a country or geographical location, for example, de, nl or dk. A ccTLD always consists out of two letters.
Root domain
The combination of only the domain name and top-level domain is known as a root domain.
While the term root domain was originally created in the context of DNS - Domain-Name Servers, it typically refers to the combination of a unique domain name and a top-level domain - extensions to form a complete website address. Your website's root domain is the highest page in your site hierarchy - probably your homepage. Individual pages or subdomains can be built off the root domain, but each page URL must technically include the same root domain in order to be a part of your website.
Subfolder
A subfolder is similar to a subdomain in that it allows you to create categories of content, but they are set up differently on servers. Unlike subdomains, there is no server partitioning involved with subfolders. A subfolder is housed on the same server and any of its link juice goes back to the domain.
Domain Name System - DNS
Domain names are formed by the rules and procedures of the Domain Name System - DNS. Any name registered in the DNS is a domain name. Domain names are organized in subordinate levels - subdomains of the DNS root domain, which is nameless. The first-level set of domain names are the top-level domains - TLDs, including the generic top-level domains - gTLDs, such as the prominent domains com, info, net, edu, org,... and the country code top-level domains - ccTLDs. Below these top-level domains in the DNS hierarchy are the second-level and third-level domain names that are typically open for reservation by end-users who wish to connect local area networks to the Internet, create other publicly accessible Internet resources or run web sites.
The registration of these domain names is usually administered by domain name registrars who sell their services to the public.
A fully qualified domain name - FQDN is a domain name that is completely specified with all labels in the hierarchy of the DNS, having no parts omitted. Labels in the Domain Name System are case-insensitive, and may therefore be written in any desired capitalization method, but most commonly domain names are written in lowercase in technical contexts.
How to choose a best Domain Name
Brandable or keyword domains?
For search engine optimization - SEO purposes, many experts recommend registering a domain with keywords you want to be found for. While this was a must years ago, it's not quite the necessity it once was.
Some people prefer to go for a shorter, brandable domain that's easier to remember - especially because so many "good" domains are taken these days.
So instead of registering a keyword-rich name like JoomlaTutorialsForBeginners.com a person may choose to go with JoomTut.com It's a made-up word from Joomla! Tutorials, but it keeps the domain short, brandable and easy to remember.
I personally think you should try to use the keywords you plan to target as long as you can keep the domain reasonably short (2-3 words) and readable. When your name is descriptive, people immediately know what your site is about.
Having said that, don't make your domain name so long and awkward.com that it's hard to read and remember. It's really about finding a balance. Also, don't be shy about bouncing ideas off your friends and family before registering.
Here's another tip. Write the name down to give you an idea of what it may look like on business cards, T-shirts and other printed materials.
Remember, your domain is a big part of your brand, so take your time coming up with the right name for your site.
We don’t recommend using anything but .com domains because everybody remembers a .com domain, and your smartphone keyboards have a pre-built key for .com
Find a domain name at NameSilo
Very cheap domain registration. That's it! And that's what makes it special. If you just want to register and manage your domains, without constant hosting, web page, email account upsells and more, NameSilo is the right place. We also offer completely free WHOIS privacy, free API access, free customizable parking options where you keep 100% of the revenue, free DNS management and much more.
Find a domain name at NameCheap
NameCheap provides a set of DNS servers spread across the US and Europe to deliver highly reliable DNS services to everyone. By choosing Namecheap.com as your domain registrar, you are choosing a highly reputable and reliable partner. Namecheap.com is rated 4.6 out of 5 - Based on 1,395 reviews via Google Checkout.
Find a domain name at Bluehost
Bluehost is a leading web hosting and domain name solutions company. Since our founding in 2003, Bluehost has continually innovated new ways to deliver on our mission: to empower people to fully harness the web. Based in Orem, Utah, we provide comprehensive tools to millions of users throughout the world so anyone, novice or pro, can get on the web and thrive with our web hosting packages.
All the good domains are taken!
As you're registering your domain, you may feel that all the names you want are taken. You just have to get creative. Website Palace has a great page that offers tips for landing a good domain name.
Usually you will have 3 options:
- Change Top-Level Domain Name to another. Such as
.com.net.org.info... - Change your domain name to another name.
- Buy premium domain from domains market
Buy premium domain from SEDO - The world's leading domain marketplace
With over 19 million listed domains, Sedo offer you the world's largest trade platform for Internet addresses. Use our convenient domain search to quickly find the domain you are searching for – or get inspired with alternative options.
- No fees or commissions for domain purchases
- Free transfer of your purchased domain
- Secure Transfer Service: funds are not released to the seller until the domain is transferred.
Buy premium domain name from NameSilo marketplace
You will find many domains at NameSilo Marketplace. These are domains that have been listed for sale by our customers, or are domains that have not been renewed. NameSilo offer two different types of sales including either auctions or an offer/counter offer sale. Depending upon the type of sale, purchase amount and the configuration options selected by the seller, you can either purchase the domain immediately, place a bid in an auction, or enter into negotiations with the seller.
Read more: How to register a Domain Name?



